How Hemorrhoids Feel and How to Manage Them with Hemorrhoid Treatments

Internal and external hemorrhoids
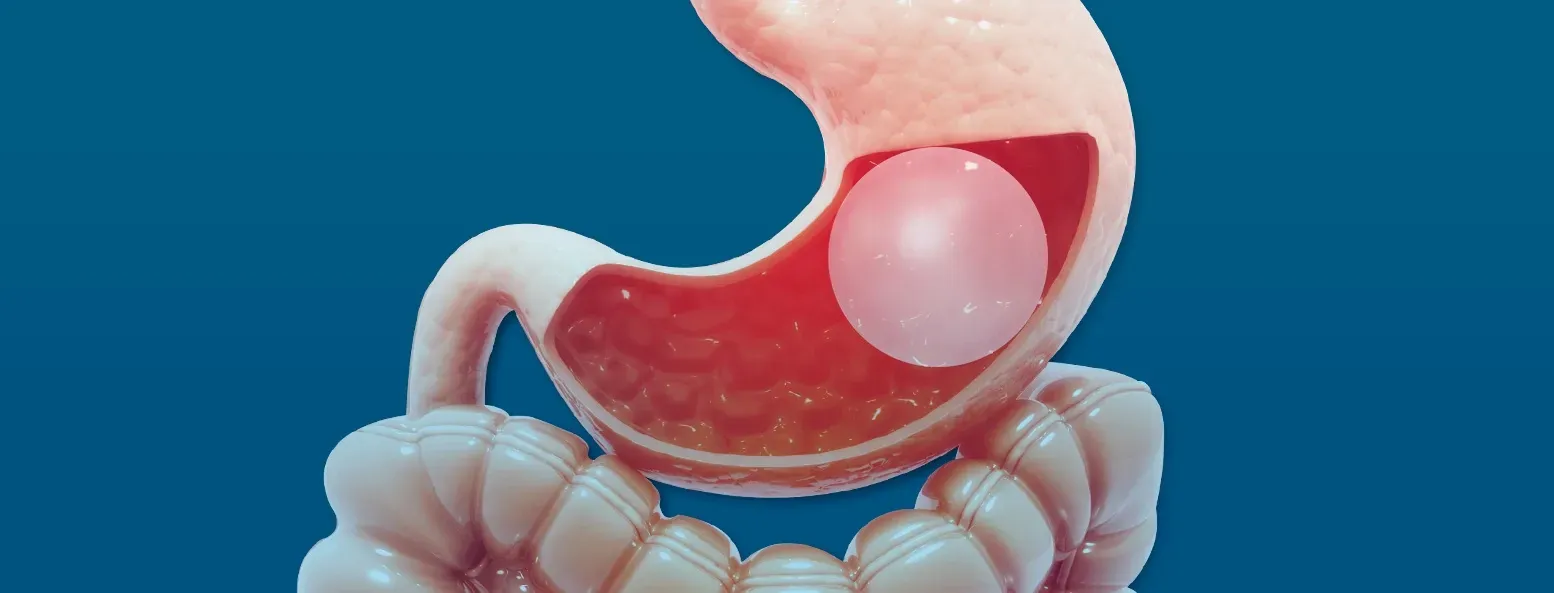
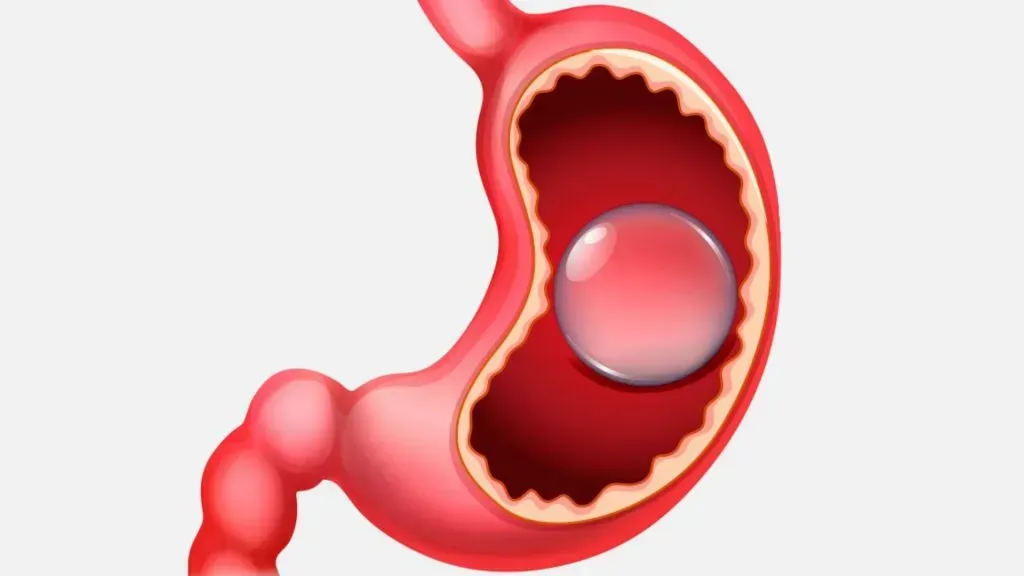
Hemorrhoids are enlarged swollen veins in the anus and rectum. They’re also called piles. They can be painful and, fortunately, there are hemorrhoid treatments.
There are two main types of hemorrhoids:
- Internal hemorrhoids are inside the rectum and may not be visible.
- External hemorrhoids are located under the skin around the anus, outside the rectum.
Hemorrhoids develop when veins in the anus and rectum widen or loose flexibility. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart. Many people have both internal and external hemorrhoids.
They’re a common condition. Almost three out of four adults will have hemorrhoids at some time.
What do hemorrhoids feel like when you’re sitting?
You may not notice that you have hemorrhoids. In other cases, you may feel:
- bleeding or spotting (often painless)
- burning
- discomfort
- itching
- pain during bowel movements
- swelling around the anus
External hemorrhoids
If you have external hemorrhoids you may feel pressure, discomfort, or a sharp pain when you sit down. You might also feel pain or discomfort during a bowel movement or when wiping the area.
Internal hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids can bleed during and after a bowl movement. You may not feel pain because they’re higher up in the rectum where there are fewer pain receptors. However, internal hemorrhoids may be pushed out through the anus while passing stool. This can trigger pain, friction, and bleeding.
What causes hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are similar to varicose veins. Varicose veins happen when the vein walls become weak and the valves that control blood flow don’t work properly. This pools blood making the vein bulge.
Hemorrhoids can happen for many reasons. The exact cause may not be known. They may be caused by pressure due to straining during bowel movements. This can happen if you suffer from long-term constipation. Sitting too much is also thought to increase your risk. Some women develop hemorrhoids during pregnancy or right after giving birth.
Hemorrhoids during pregnancy
Up to 35 percent of women have hemorrhoids during pregnancy. This may be due to hormonal changes and raised blood pressure during pregnancy. Hemorrhoids are more likely during the third trimester (at the end) of pregnancy, when women are carrying more weight from the growing baby.
Some women develop hemorrhoids shortly after giving birth. This is more common in a vaginal delivery because of the immense pressure on the veins in the abdomen (stomach) and pelvic area.
Call your primary doctor, or gastroenterologist , if you have difficulty with bowel movements by the third or fourth day after delivery. Constipation is common after giving birth. It does not mean that you’ll develop hemorrhoids.
In most cases, hemorrhoids that happen during pregnancy or delivery heal on their own shortly after giving birth.
Hemorrhoids will not affect the baby during pregnancy or birth.
Treatment for hemorrhoids
In most cases, hemorrhoids shrink on their own or with at-home treatments. Lifestyle changes that keep you regular can help. Easier bowel movements without straining are the primary way to prevent hemorrhoid flare-ups. They will also reduce your risk of developing them.
Tips on adding fiber to your diet
- Add more fiber-rich foods such as fresh fruit, vegetables, and whole grains to your diet.
- Eat prunes, they’re a natural and mild laxative (stool softener).
- Take a fiber supplement, such as psyllium husk. This adds bulk and softens bowel movements, so you don’t have to strain.
- Add fiber to your daily diet slowly to help avoid gassiness.
- Staying hydrated is especially important if you’re adding more fiber to your diet.
Ideas to make bowel movements easier
Add a tablespoon of mineral oil to your food. Mineral oil helps to ease constipation.
Drink at least 8 to 10 glasses of water and other hydrating (non-caffeinated) fluids throughout the day. It helps to prevent worsening constipation.
Change your toilet habits. Don’t delay going to the bathroom. Putting off a bowel movement can make you more constipated and worsen symptoms. Use a small stepping stool to prop your feet up when you sit on the toilet. This angles your body into a squatting position, making it easier to have a bowel movement.
Tips to manage hemorrhoids
If you have hemorrhoid symptoms, several options can help soothe flare-ups:
- avoid dry toilet paper, use a damp wipe or water to wash
- avoid perfumed or alcohol wipes
- avoid sprays, deodorants, or douches in the groin area
- avoid strenuous exercise and other activities that cause friction
- avoid tight clothing and rough fabrics
- keep the area clean
- use numbing (lidocaine) creams
- take pain medication as needed, like acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- sit on a reclining or rocking chair rather than sitting upright
- sit on a soft pillow or donut cushion
- soak in a warm water bath
- try topical treatments, such as creams, ointments, sprays and suppositories with hydrocortisone
- use ice packs or cold compresses
- Apply witch hazel with a cotton pad
Procedures for hemorrhoids
In some cases, your doctor may recommend a medical procedure to prevent more serious complications. Complications include blood clots, inflammation, and infection.
Hemorrhoids are a condition treated by a gastroenterologist and that treatment depends on the type of hemorrhoid and complication you have. You may need treatment more than once. Procedures for hemorrhoids include:
Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy injections may be used to treat external and internal hemorrhoids. Your doctor will inject the hemorrhoid with a chemical solution that causes it to shrink. This may take a few days. Sclerotherapy injections are also used to treat small damaged veins in other area of the body.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy (freezing therapy) focuses cold air or gas on the hemorrhoid to shrink it.
Laser treatment
Laser treatment may be used to treat internal hemorrhoids. They work by hardening the blood inside the hemorrhoid. This causes it to shrivel. Heat and light therapy may also be used to treat hemorrhoids in the same way.
Thromboectomy
External hemorrhoid thromboectomy is a procedure to remove a blood clot in an external hemorrhoid. Your doctor will numb the area, make a small cut and drain it. You may need stitches in the area depending on how large the cut is.
Band ligation
Internal hemorrhoid rubber band ligation is a procedure where one or more tiny rubber bands are placed around the base of an internal hemorrhoid. This cuts off the blood circulation. The hemorrhoid shrinks away within a week.
Surgery
If other treatments do not work or if the hemorrhoid is very large, your doctor may recommend minor surgery to remove it. You may need local or general (full) anesthesia for this. There are two main types of surgeries for hemorrhoids.
- Hemorrhoidectomy (hemorrhoid removal) involves removing all the extra tissue that’s causing the hemorrhoid. This is used to treat both internal and external hemorrhoids.
- Hemorrhoid stapling is a procedure in which a surgical staple is placed to block blood flow to the hemorrhoid. This shrinks it completely. Stapling is used to treat internal hemorrhoids.
Medications for hemorrhoids
Over-the-counter medications can be used to treat mild hemorrhoid symptoms. These include:
- witch hazel
- hydrocortisone cream, ointment, or suppositories (use for no more than a week unless otherwise directed by your doctor)
- lidocaine
- laxatives (stool softeners)
Your doctor may also prescribe an antibiotic if there’s a concern for infection.
Hemorrhoids are common and treatable
Hemorrhoids are common in adults. In most cases, they aren’t serious and heal on their own.
Tell your doctor immediately if your hemorrhoid symptoms do not go away after a week, or sooner if you experience severe pain or bleeding. Your doctor may need to examine the area to make sure you don’t have complications. You may also need additional treatment.
If you have hemorrhoids while pregnant or nursing, your doctor may wait to treat you with medications or procedures.
You can help ease your discomfort with natural treatment such as fiber-rich foods and supplements. Drink plenty of water, sit in a warm bath, and apply natural remedies such as witch hazel compresses to soothe the area. Talk to your doctor before using any over-the-counter cream for hemorrhoids.
Read More About Hemorrhoids Diagnosis and treatment
Learn About Thrombosed Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids Diagnosis and treatment
Symptoms of hemorrhoids that you must identify
What Causes Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids and Hemorrhoid Treatment
The post How Hemorrhoids Feel and How to Manage Them with Hemorrhoid Treatments appeared first on Gastro SB.