Ask the Gastroenterologist: What is a Hiatal Hernia?
What is Hiatal Hernia?
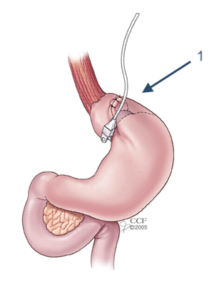
Any time an internal body part pushes into an area where it doesn’t belong, it’s called a hernia. The hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm — the muscular wall separating the chest cavity from the abdomen. In a hiatal hernia (also called hiatus hernia) the stomach bulges up into the chest through that opening. It is a condition that can be diagnosed by your gastroenterologist with a series of tests.
There are two main types of hiatal hernias: sliding and paraesophageal (next to the esophagus).
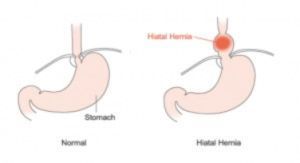
In a sliding hiatal hernia, the stomach and the section of the esophagus that joins the stomach slide up into the chest through the hiatus. This is the more common type of hernia.
The paraesophageal hernia is less common but is more cause for concern. The esophagus and stomach stay in their normal locations, but part of the stomach squeezes through the hiatus, landing it next to the esophagus. Although you can have this type of hernia without any symptoms, the danger is that the stomach can become “strangled,” or have its blood supply shut off.
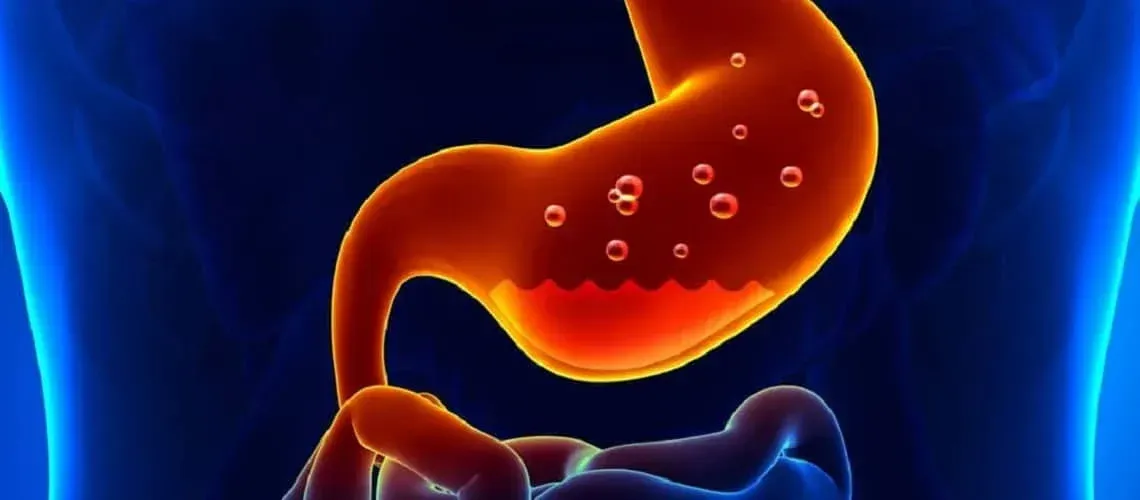
Often, people with hiatal hernia also have digestive issues , like heartburn or acid reflux disease. Although there appears to be a link, one condition does not seem to cause the other.
What Are The Causes of Hiatal Hernia?
Most of the time, the cause is not known. Some people develop a hiatal hernia after sustaining an injury to that area of the body; others are born with a weakness or an especially large hiatus. Increased pressure in the abdomen from coughing, straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, and delivery, or substantial weight gain may contribute to the development of a hiatal hernia. In addition to the increased occurrence in people over fifty, hiatal hernias also occur more often in overweight people (especially women) and smokers.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms of Hiatal Hernia?
Most small hiatal hernias cause no signs or symptoms. Larger hiatal hernias can cause:
- Heartburn
- Regurgitation of food or liquids into the mouth
- Acid reflux
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chest or abdominal pain
- Shortness of breath
- Vomiting of blood or passing of black stools, which may indicate gastrointestinal bleeding
What Are The Risk Factors of Hiatal Hernia?
Hiatal hernia is most common in people who are:
- Age 50 or older
- Overweight
How is Hiatal Hernia Diagnosed?
A hiatal hernia can be diagnosed with a specialized X-ray study that allows visualization of the esophagus (barium swallow) or with an upper endoscopy.
What Are Possible Treatments For Hiatal Hernia?
Most people do not experience any symptoms of their hiatal hernia so no treatment is necessary unless there are symptoms of acid reflux disease. However, the para-esophageal hernia (when part of the stomach squeezes through the hiatus) can cause the stomach to be strangled so surgery is usually recommended.
Do you know what the difference is between a gastroenterologist and a colorectal surgeon?
While we treat many of the same conditions there are some inherent differences in these two specialties. Knowing this difference will guide you to the right specialist.
A colorectal surgeon, may also be known as a proctologist. That’s what I am. To become a colorectal surgeon, you must first become a general surgeon, which includes 5 years of surgical residency after medical school, where you learn how to do all sorts of surgeries from gallbladder surgery, hernia surgery, breast surgery, and even vascular surgery. You then do an extra year of specialty surgical training in colon and rectal surgery to become an expert in surgery for the colon, rectum and anus treating everything from hemorrhoids and anal fistulas to colorectal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, diverticulitis and pelvic floor disorders. During that time you also learn to perform colonoscopy and endoluminal procedures. Many colorectal surgeons practice both general surgery and colorectal surgery, and some choose to specialize only in colorectal surgery (me), despite being board certified in both.
Gastroenterologists, on the other hand, first complete 3 years of medical residency, learning to care for all medical conditions from diabetes and heart disease to pneumonia and rheumatoid arthritis. They then do 3 years of specialty training in the medical management of gastrointestinal diseases and learn to do colonoscopy and endoscopy. Some do an extra year of training in inflammatory bowel disease, liver disease, or advanced endoscopy as an example. While most GI doctors do endoscopic procedures they don’t don’t operate on patients. So a small polyp found at the time of your colonoscopy by a gastroenterologist may be removed by your GI doc, but if you have a polyp that is so large that it can’t be removed endoscopically, you may be referred to a surgeon. You will also be referred to a colorectal surgeon if you have a colon cancer.
While the conditions that colorectal surgeons and gastroenterologists treat may overlap (we both may do colonoscopies for example) there are some key differences in the treatments we offer by trade, and some may be provider- or institution-specific.
- Colorectal surgeons, generally don’t treat stomach, pancreas, liver disease – gastroenterologist do. If you need a surgeon for those conditions, they may refer you to a surgeon specialist in those areas.
- Since Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a GI symptom , and is never a surgical condition, that’s also in the realm of of the GI.
- Colorectal surgeons also generally don’t employ medical treatment of inflammatory bowel disease – that’s generally done by GI in the US and a referral to surgery is made only when the condition is bad enough to need surgery.
- Colorectal surgeons often do more than just surgery, especially when it comes to anal disease. We offer non-surgical approaches to hemorrhoids and anal fissure and only if the condition gets serious enough do we escalate treatment to surgery.
- The breadth of treatments we offer from office based to surgical allows us to choose the best treatment based on your condition, not simply due to a lack of expertise in surgery.
I hope this post helps clarify any confusion about these specialties and helps get you to the best provider for your condition. If you are unsure who you should be seeing, it’s best to ask before you make you appointment to avoid any confusion or disappointment at the time of your consultation!
The post Ask the Gastroenterologist: What is a Hiatal Hernia? appeared first on Gastro SB.